Israel-Iran War 2026 Effects: Casualties, Countries Involved, Oil Price Surge & Global Reactions – Live Updates
Israel-Iran War 2026 Effects: Casualties, Countries Involved, Oil Price Surge & Global Reactions – Live Updates

Introduction: The Escalating Crisis in the Middle East
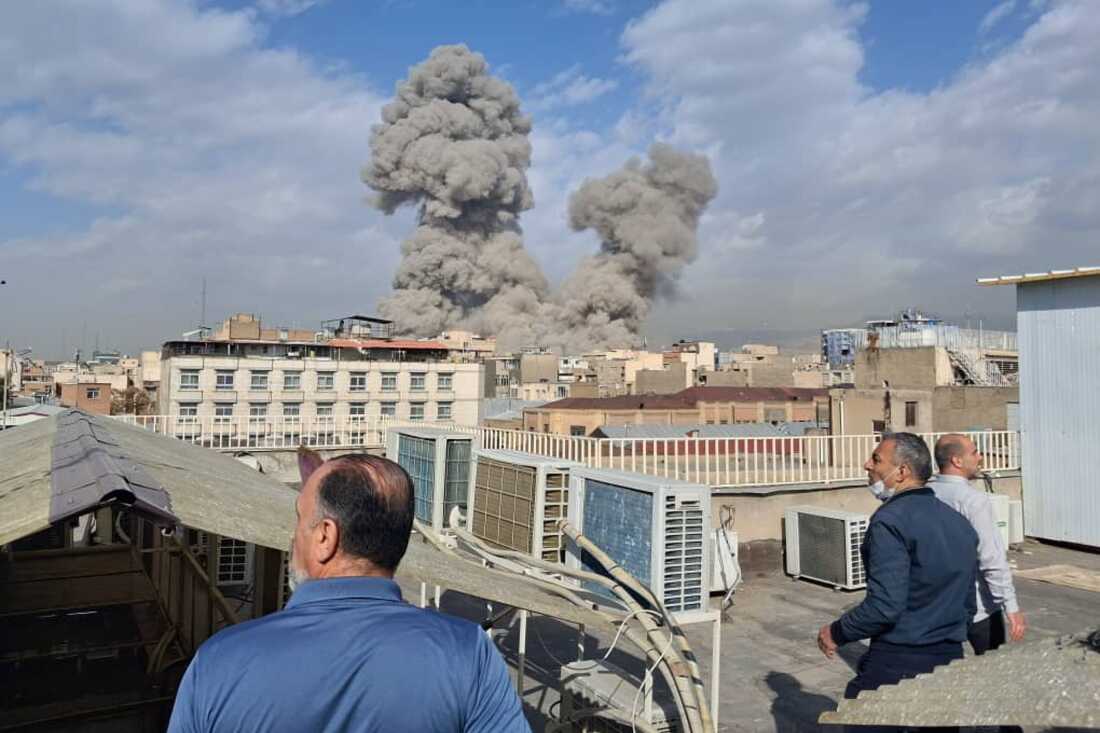
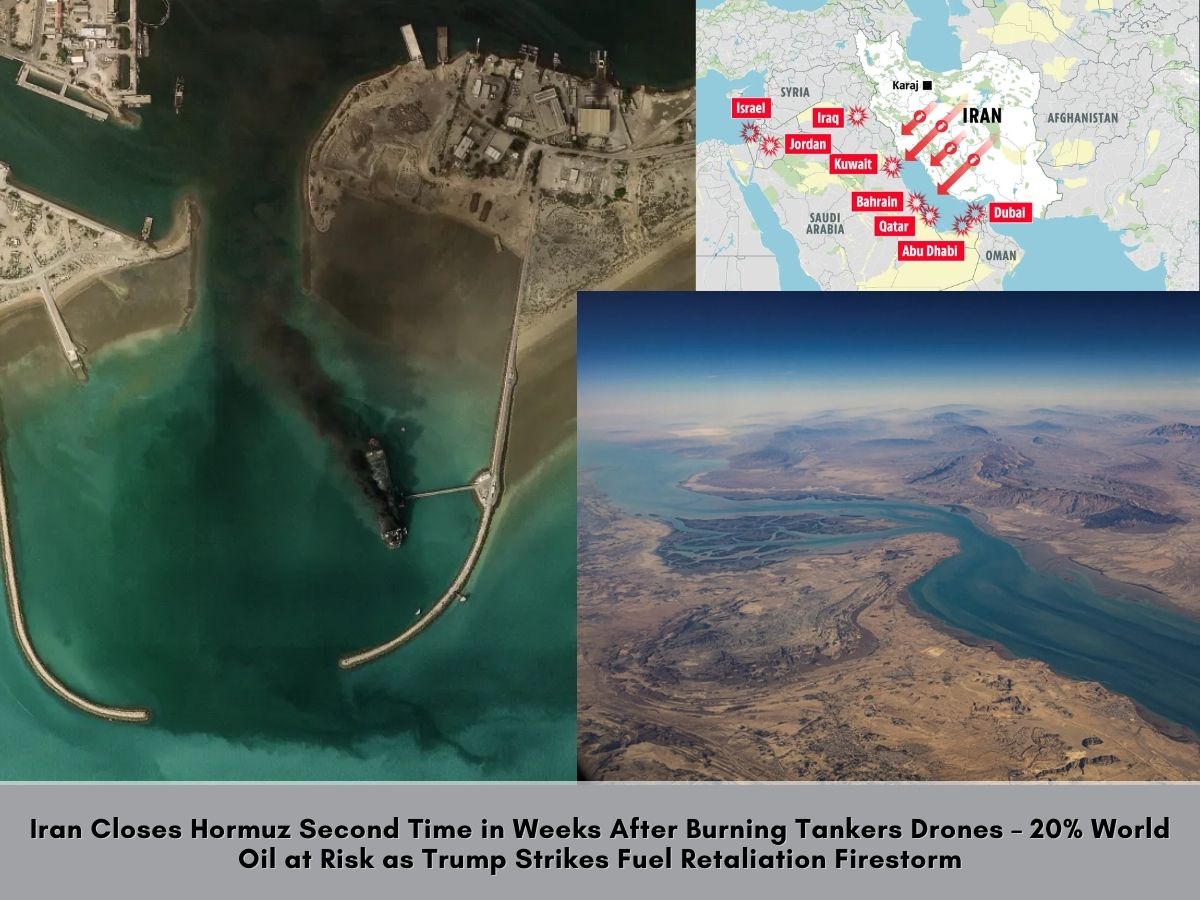
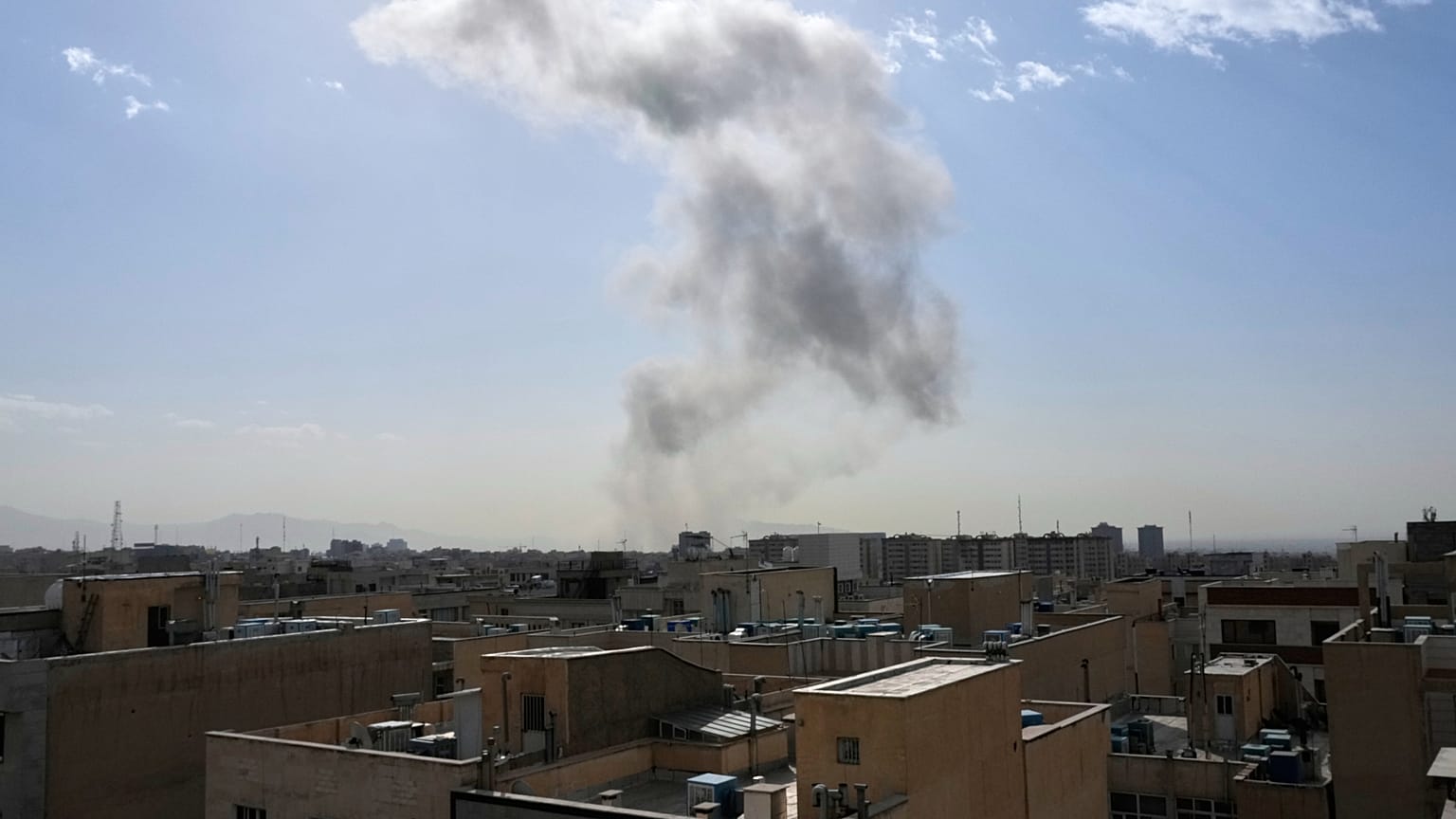
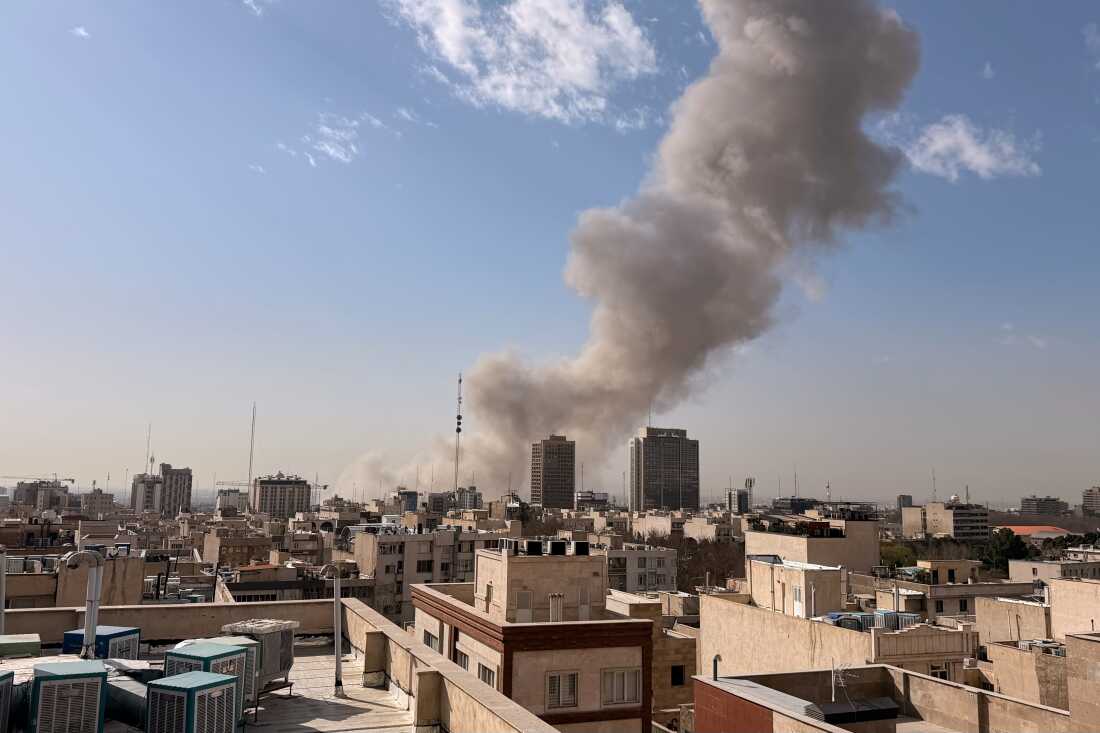
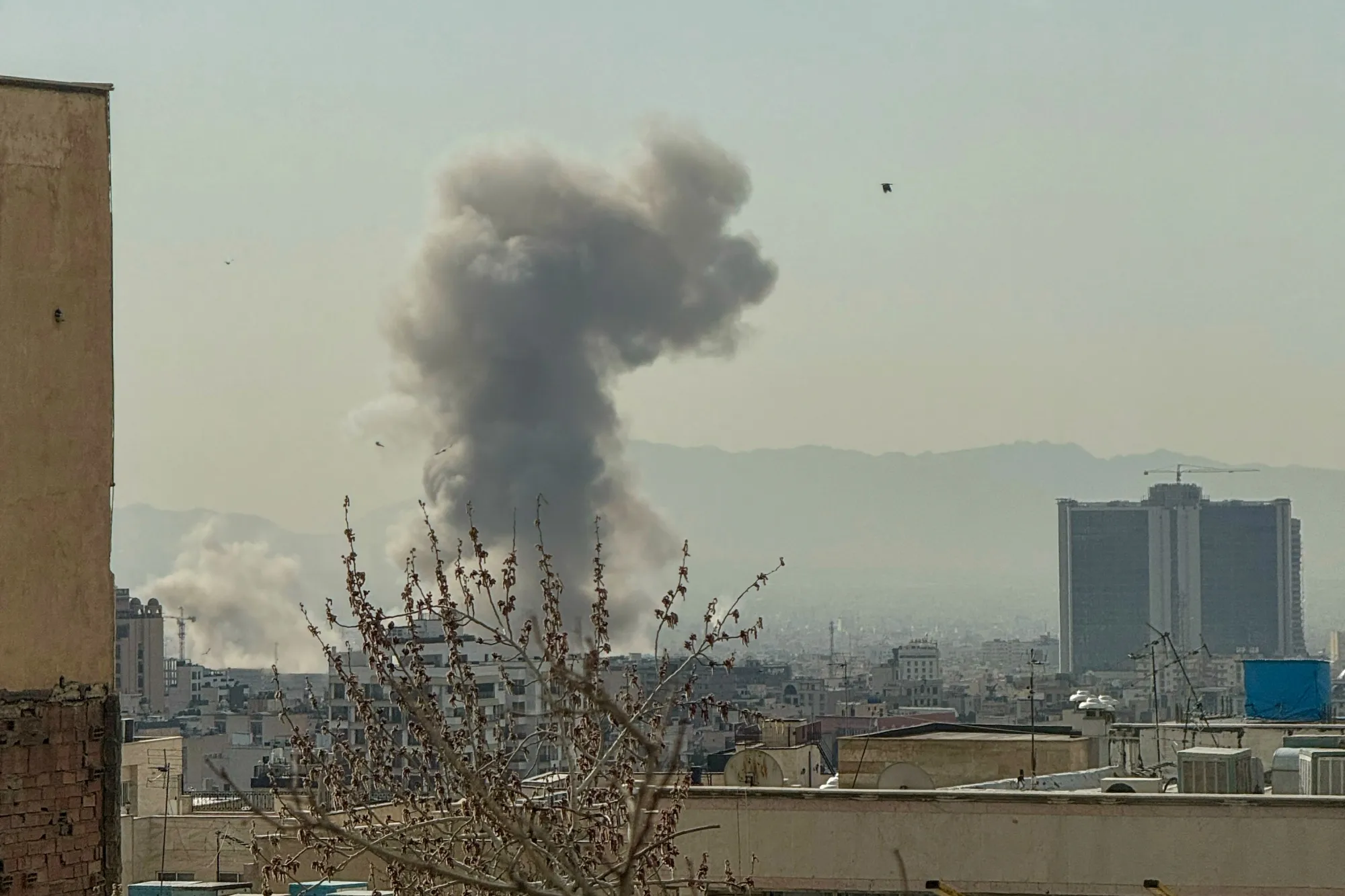
The Israel-Iran War of 2026, which erupted on February 28 with preemptive strikes by Israel and the United States on Iranian targets, has rapidly evolved into a multifaceted conflict with profound global repercussions. This war marks a significant escalation from previous tensions, including the 2024 and 2025 exchanges, and has drawn in multiple countries while inflicting heavy casualties and economic disruptions. As explosions rocked Tehran and air raid sirens wailed across Israel, the world watches a conflict that threatens regional stability, spikes oil prices, and reshapes international alliances.
For the latest breaking news on the initial strikes, check our War Update 1: Israel Strikes Iran February 28 2026.
Rooted in decades of animosity over Iran's nuclear program, support for proxy militias, and regional dominance, this war has already caused thousands of casualties, displaced populations, and triggered a humanitarian crisis. Countries directly involved include Israel, Iran, and the United States, with indirect roles played by proxies like Hezbollah in Lebanon, Houthis in Yemen, and militias in Iraq and Syria. Global reactions range from condemnation to support, as evidenced by real-time tweets and protests worldwide. This article examines the effects, casualties, involved nations, and broader implications, incorporating verified images and social media insights for a comprehensive view.
Countries Involved: A Web of Alliances and Proxies
The core combatants are Israel and Iran, but the conflict's scope extends far beyond their borders. Israel, supported by the United States, launched the initial strikes, citing imminent threats from Iran's nuclear advancements and missile programs. The U.S. role has been pivotal, providing intelligence, military aid, and direct participation in bombing campaigns against Iranian nuclear sites like Natanz and Fordow. As per reports from the Council on Foreign Relations, the U.S. intervention aims to prevent Iran from acquiring nuclear weapons, marking the first direct American attack on another country's nuclear program.
Iran, on the other hand, has mobilized its "Axis of Resistance," a network of proxy groups including Hezbollah in Lebanon, Houthis in Yemen, and Shia militias in Iraq and Syria. These proxies have launched retaliatory attacks on Israeli and U.S. targets, expanding the conflict. For instance, Hezbollah's missile barrages from Lebanon have targeted northern Israel, while Houthi drones have disrupted shipping in the Red Sea. Other nations indirectly involved include Jordan, which intercepted Iranian missiles, and Gulf states like Saudi Arabia and the UAE, who shared intelligence with Israel despite public condemnations.
Russia has criticized the U.S. strikes, providing diplomatic support to Iran, while China has called for de-escalation amid concerns over oil supplies. European countries, including France and the UK, have assisted in intercepting attacks but urged restraint. The map below illustrates the territories with Iran-backed militias and key strike locations.

According to Wikipedia and CSIS analyses, the conflict's expansion risks drawing in more states, potentially leading to a broader regional war involving Turkey, which has boosted its missile arsenal in response, and Pakistan, offering support to Iran.
Learn more about the preemptive strikes that started it all in our detailed coverage of Israel strikes on Iran February 28 2026.
Casualties: The Human Toll of the Conflict
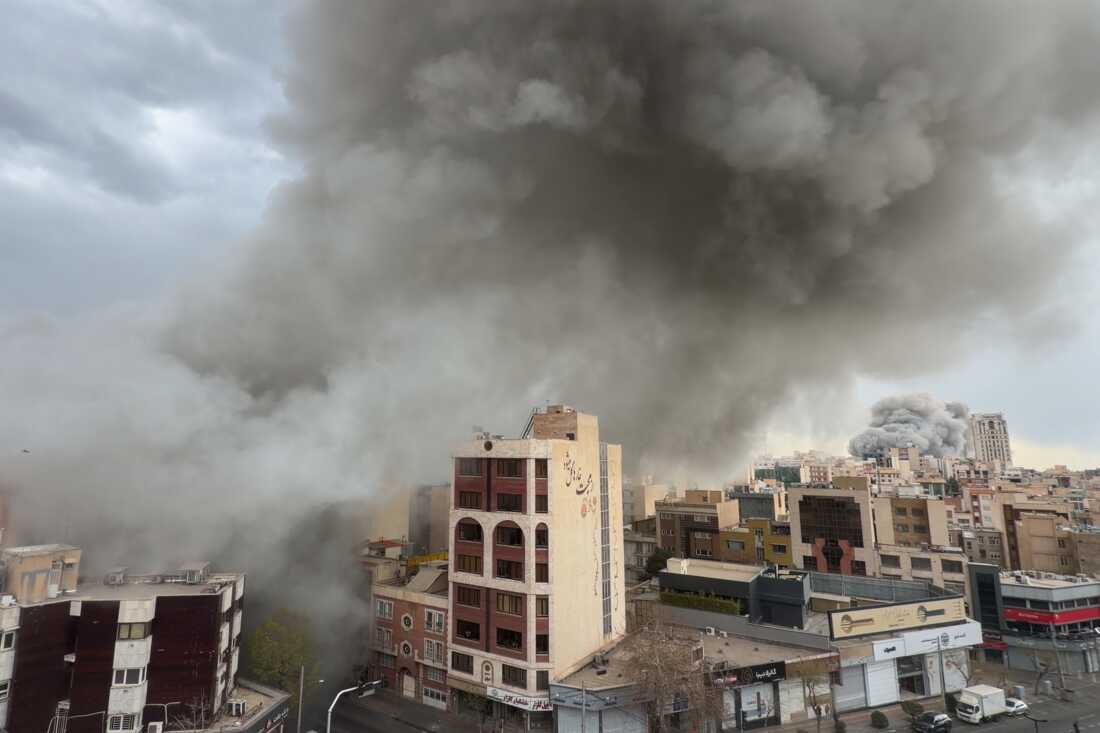
As of February 28, 2026, the war has inflicted significant casualties on both sides, though exact figures remain contested due to information blackouts and propaganda. Initial reports from the Times of Israel indicate that Iranian ballistic missile attacks on Israel have killed at least 28 people, mostly civilians, and wounded over 3,000. In one barrage, 550 missiles and 1,000 drones were fired, with impacts in populated areas like Tel Aviv and Haifa causing 31 strikes and dozens of fatalities.
On the Iranian side, Israeli and U.S. strikes have resulted in higher casualties. Iran's army reported four soldiers killed in initial October 2024-like strikes, but the 2026 escalation has seen estimates soar. The Associated Press and Al Jazeera report that strikes on military bases, nuclear facilities, and Tehran have killed at least 16 Iranian officers, proxy fighters, and civilians, with unconfirmed reports of hundreds more from collapsed infrastructure and secondary explosions. A notable incident involved the death of senior IRGC commanders, echoing the 2024 killing of Mohammad Reza Zahedi.
Civilian casualties are particularly alarming. In Israel, a Palestinian laborer was killed by debris, and in Iran, collateral damage to schools and restaurants has injured dozens. The Health Ministry in Israel reports 3,238 hospitalizations, including for anxiety. Proxy conflicts have amplified the toll: Hezbollah clashes have killed dozens in Lebanon, while Houthi actions in Yemen add to regional deaths. Overall, estimates from ACLED and CSIS suggest thousands dead and wounded, with potential for tens of thousands if escalation continues.

The International Institute for Strategic Studies notes that Iran's missile strategy has led to higher Israeli casualties in urban areas, with 23 killed and 600 injured in recent barrages, highlighting the war's devastating human cost.
Economic Effects: Oil Price Surges and Global Market Volatility
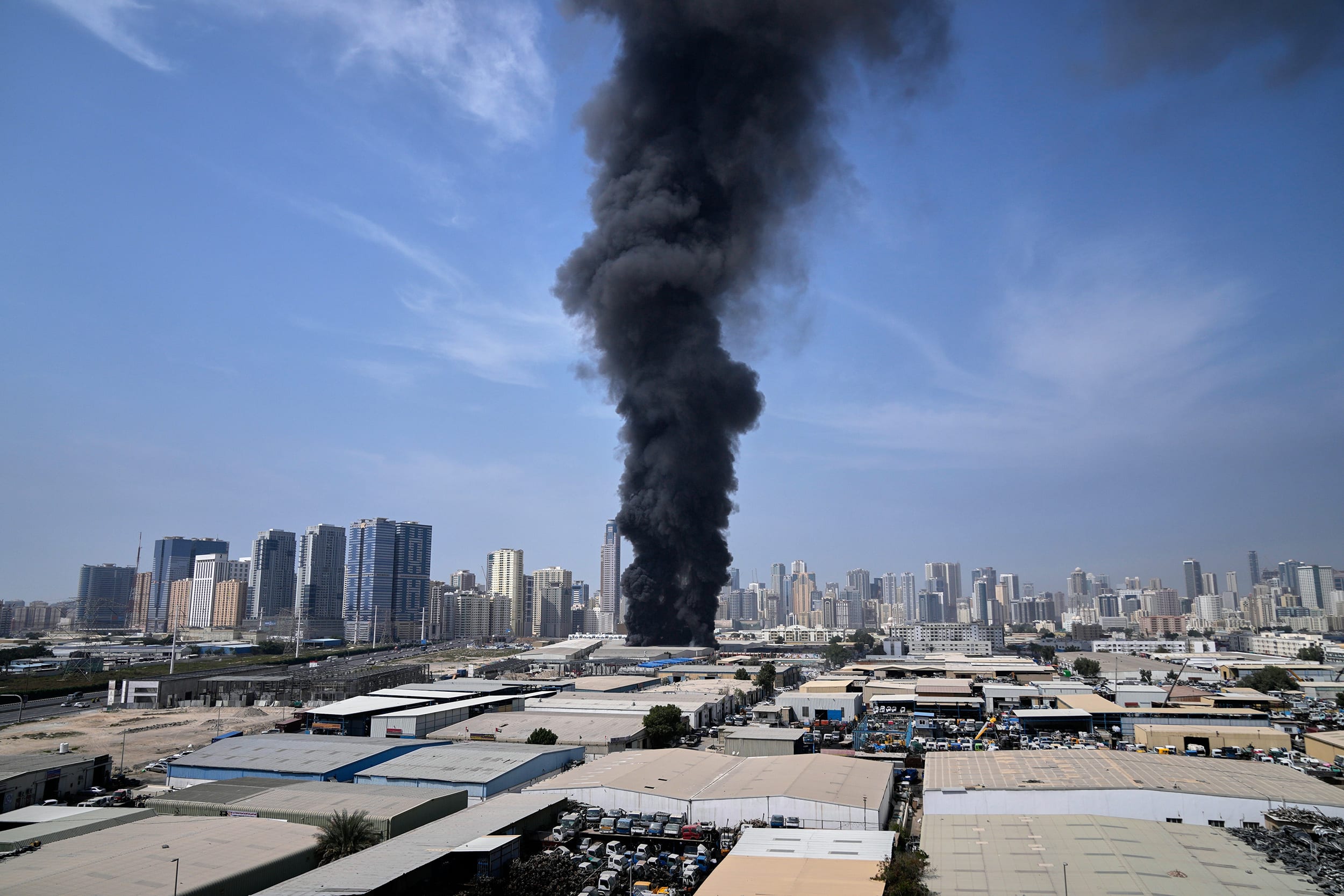
The war's economic ramifications are immediate and far-reaching. As a major oil producer, Iran's involvement has disrupted global energy markets. The Strait of Hormuz, through which 35% of seaborne oil and 20% of LNG pass, faces closure threats, pushing Brent crude prices above $100 per barrel, per Goldman Sachs estimates. This surge, up 17% during initial strikes, could lead to $120-$150 per barrel in a full-scale war, triggering global inflation and recessions.
According to the Washington Institute and Columbia University's Energy Policy Center, U.S. shale producers benefit from secured prices, but Gulf states like Saudi Arabia face risks to infrastructure. Oil prices hit $81.40 post-strikes, with potential drops below $60 if tensions ease, but current volatility affects sectors worldwide. The conflict has cost Iran $17.8 billion in damages (3.3% of Israel's GDP equivalent impact), straining its economy already weakened by sanctions.
Israel's economy shows resilience, with the Tel Aviv Stock Exchange up 67% since October 2023 attacks and GDP growth projected highest among developed nations at $57,000 per capita. However, insurance disruptions and airspace closures impact aviation and trade. Globally, higher energy bills feed inflation, as noted by the BBC, potentially halting economic activity amid supply chain collapses.
The RUSI commentary highlights compounding crises with Russia and Houthis, increasing oil market shocks. J.P. Morgan notes a $7.5 geopolitical risk premium on Brent crude, with potential for $100+ if Hormuz is blockaded.
For real-time updates on how the strikes began, visit our Israel-Iran war update on February 28 strikes.
Regional and Global Stability: Broader Geopolitical Shifts
The war threatens Middle East stability, risking spillover into Iraq, Syria, Lebanon, and Yemen. Iran's proxies have imposed costs, with over 500 missiles launched at Israel in 2025 analogs, causing casualties. ACLED warns of Iranian retaliation targeting U.S. interests, complicating U.S. presence in the region.
Global reactions vary: The UN calls for ceasefire, Europe expresses concern, and oil-dependent nations like China face supply fears. Protests erupt worldwide, with Iranian expatriates calling for regime change, while supporters rally against Israel. In the U.S., divisions emerge, with Trump justifying strikes but critics like Rep. Thomas Massie decrying unauthorized war.

Second-order effects include Turkey arming missiles, Pakistan supporting Iran with visas for pilgrims, and Azerbaijan shifting sentiment. India's ties with Iran suffer from spying allegations, potentially reshaping alliances. The Atlantic Council notes Arab states' reluctant support for Israel, tied to U.S. bases, while emphasizing the need for diplomacy to prevent wider war.
Real-Time Insights from Social Media: Tweets Capturing the Chaos
Social media provides raw, unfiltered perspectives on the war's effects. Here are selected tweets reflecting casualties, reactions, and calls for peace:
These tweets underscore the economic strains, human costs, and geopolitical shifts, with users debating regime change and war's futility.
Analysis: Long-Term Implications and Path to Resolution
The war's effects could persist for years. Economically, sustained high oil prices risk global recession, as per ICIS scenarios. Geopolitically, it may realign alliances, with Arab states balancing U.S. ties and public sentiment. Humanitarian crises in displaced populations demand international aid.
For resolution, diplomacy is key. The U.S.-brokered ceasefire in 2025 offers a model, but Iran's enriched uranium stockpile and missile capabilities complicate talks. Experts from the Economics Observatory warn of stagflation risks, emphasizing de-escalation to avert broader conflict.

Conclusion: A Call for Peace Amid Uncertainty
The Israel-Iran War 2026 has unleashed devastating effects, from mounting casualties to economic turmoil and geopolitical upheaval. With Israel, Iran, the U.S., and proxies entangled, the path forward requires urgent diplomacy to prevent further loss. As global reactions via tweets and protests show, the world demands an end to this cycle of violence. Follow for updates on this evolving crisis.
Read our initial report on the
Breaking: Israel Launches Preemptive War on Iran - Strikes Hit Tehran on February 28, 2026
Breaking: Israel Launches Preemptive War on Iran - Strikes Hit Tehran on February 28, 2026

Introduction to the Israel-Iran Conflict Escalation
In a dramatic escalation that has sent shockwaves across the globe, Israel has initiated a preemptive military strike against Iran on February 28, 2026. According to statements from Israeli Defense Minister Israel Katz, the operation was launched to neutralize imminent threats from Iran, including potential missile attacks and nuclear advancements. This marks the second major confrontation between the two nations in less than a year, following the brief but intense Twelve-Day War in June 2025.
Reports from multiple sources, including CNN, Reuters, and The New York Times, confirm that explosions rocked Tehran early this morning, with smoke plumes visible across the city's skyline. The United States has been implicated in the strikes, with anonymous officials stating that American forces participated in the joint operation. This development has raised fears of a broader regional war, potentially involving other Middle Eastern powers and even global superpowers.
As of 12:36 PM IST, air raid sirens blared across Israel, and a state of emergency was declared nationwide. Civilian flights have been suspended in both Israel and Iran, and international markets are reacting with volatility, particularly in oil prices. This article delves into the background, details of the strikes, international reactions, and potential implications, drawing from real-time tweets and verified images to provide a comprehensive overview.
Background: From Proxy Conflicts to Direct War
The tensions between Israel and Iran have simmered for decades, rooted in ideological differences, regional power struggles, and Iran's support for proxy groups like Hezbollah and Hamas. The proxy war escalated into direct confrontation in June 2025, when Israel bombed Iranian nuclear facilities, leading to the Twelve-Day War. That conflict ended in a fragile ceasefire under U.S. pressure, but underlying issues—particularly Iran's nuclear program—remained unresolved.
According to the Critical Threats Project, Iran had amassed over 400 kilograms of uranium enriched to 60% before the 2025 war. Post-ceasefire, Iran continued to reject zero-enrichment demands and rebuilt parts of its ballistic missile infrastructure, including protective structures at sites like Khojir and Parchin. These developments, coupled with threats from Iranian-backed militias in Iraq and Syria, prompted Israel to act preemptively.
In the lead-up to today's strikes, U.S. President Donald Trump issued warnings to Iran, amassing forces in the Middle East. Negotiations in Geneva faltered, with Iran refusing U.S. demands to dismantle nuclear facilities. On February 27, 2026, reports from ACLED highlighted the looming threat, predicting a potential U.S.-Israel joint operation if diplomacy failed.
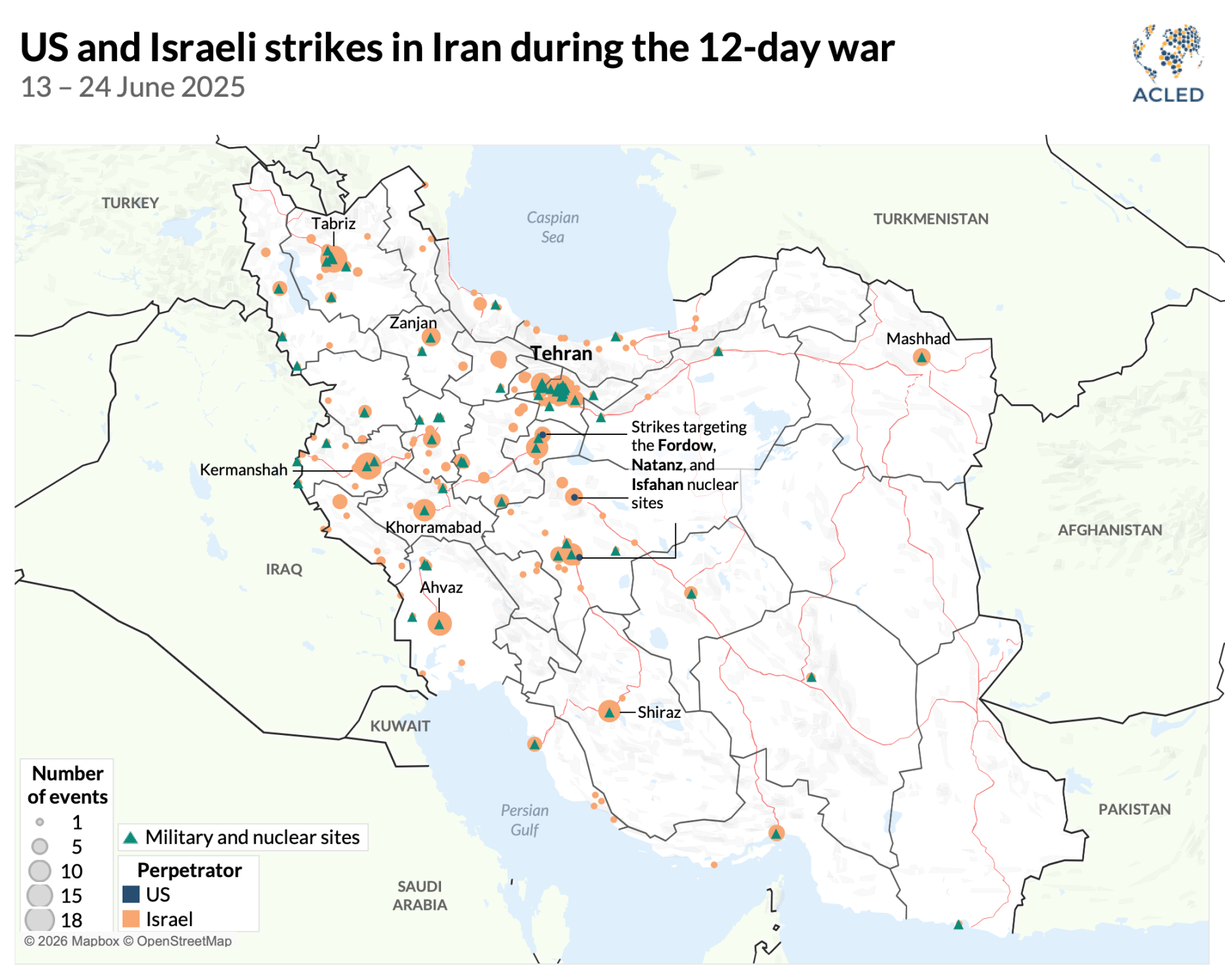
The 2025 war saw over 380 Israeli strikes on Iranian targets, killing senior commanders and destroying key assets. However, Iran retained its enriched uranium stockpile and technical expertise, setting the stage for today's events. Experts like those from the Institute for Science and International Security note that sites like Taleghan 2 were hardened against airstrikes, making a repeat operation more challenging.
Details of the February 28, 2026 Strikes
The strikes began around 1:28 AM ET (approximately 11:58 AM IST), with Israeli and U.S. forces targeting military installations in Tehran and other provinces. Witnesses in Tehran reported multiple explosions, with smoke rising from central areas, including near the presidential office. Al Jazeera confirmed that air raid sirens were activated in Israel in anticipation of Iranian retaliation via drones and ballistic missiles.
Reuters reported that the operation aimed to "remove threats to the State of Israel," focusing on missile production complexes and nuclear-related sites. A U.S. official told Al Jazeera that the strikes were joint, pushing the Middle East into renewed confrontation. Visual evidence from Tehran shows thick smoke columns against the city skyline, corroborating reports of direct hits.
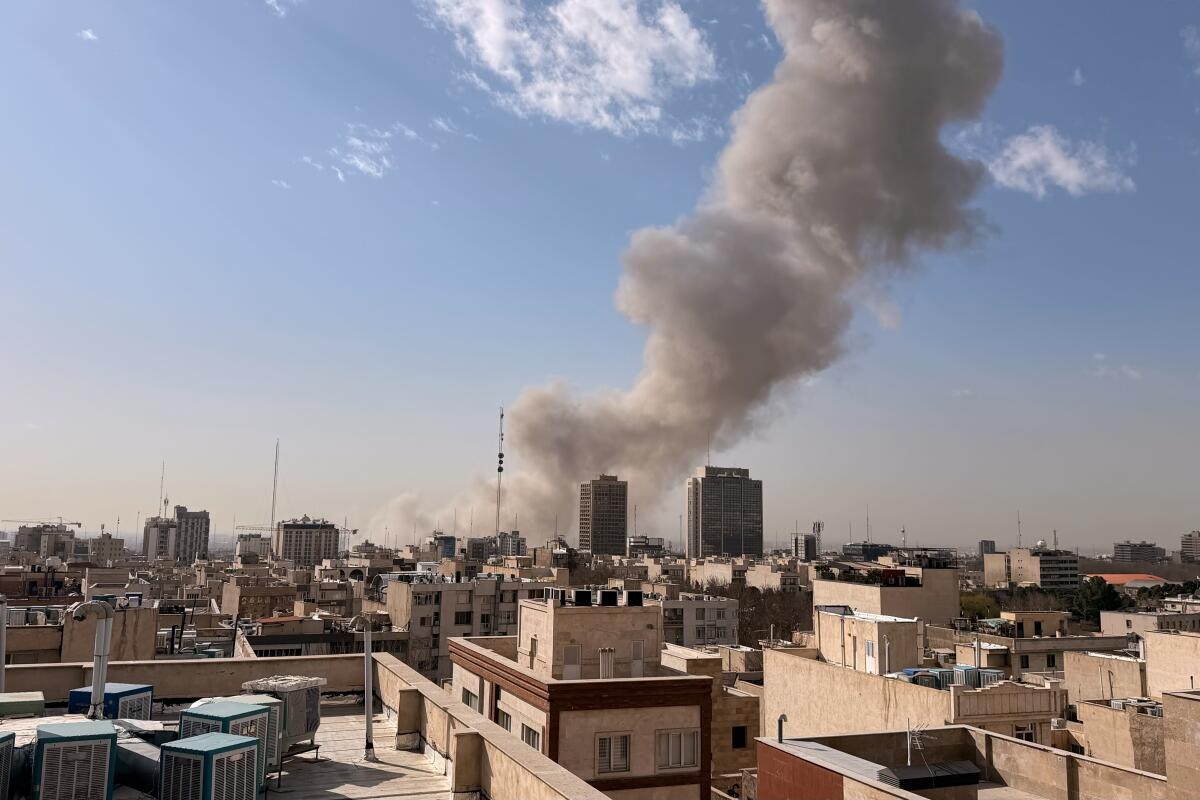

According to The Associated Press, the U.S. participation marks a significant escalation, unauthorized by Congress as noted by Representative Thomas Massie. Iranian state media has yet to confirm casualties, but initial estimates suggest damage to key infrastructure. Israel's military sounded protective air raid sirens nationwide, preparing for possible incoming missiles.
This operation echoes the 2025 strikes, where the U.S. targeted Iran's three main nuclear facilities. However, today's attacks appear more targeted at command centers in Tehran, potentially aiming to decapitate leadership or disrupt retaliation capabilities.
Global and Regional Reactions
The international community has reacted swiftly. The United Nations called for an immediate ceasefire, while European leaders expressed concern over regional stability. Oil prices surged by 5% in early trading, reflecting fears of disrupted supplies from the Persian Gulf.
In the U.S., political figures are divided. President Trump justified the strikes as necessary to prevent Iran from acquiring nuclear weapons, but critics like Massie decried them as "acts of war unauthorized by Congress." Iranian officials vowed retaliation, with state media reporting mobilization of forces.
Protests and demonstrations have erupted worldwide. In Israel, supporters rallied with banners reading "Brave People of Iran, Israel Stands With You Until Freedom." Iranian expatriates echoed calls for regime change, hoping the strikes weaken the Islamic Republic.

ACLED experts warn that Iran could impose significant costs, as seen in the 2025 war when over 500 missiles were launched at Israel, causing dozens of casualties. Iraqi militias like Kataib Hezbollah threatened attacks on U.S. interests, complicating the situation further.
Real-Time Updates from Social Media
Social media platforms, particularly X (formerly Twitter), are abuzz with eyewitness accounts and analyses. Here are some key tweets capturing the moment:
These tweets reflect the rapid dissemination of information and public sentiment, ranging from alarm to calls for regime change in Iran.
Analysis: Potential Outcomes and Global Impact
The strikes could lead to several scenarios. A limited exchange might end with another ceasefire, but Iran's threats of unrestricted response suggest escalation. Experts predict Iranian retaliation targeting Israeli cities like Tel Aviv and Haifa, potentially causing thousands of casualties.
Economically, disruptions in the Persian Gulf could spike oil prices, affecting global markets. Geopolitically, involvement of powers like Russia or China could broaden the conflict. The U.S.'s role raises domestic debates on congressional authorization for war.
For Israel, this is a high-stakes gamble to curb Iran's nuclear ambitions. Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu, a long-time advocate against Iran's program, stated Israel would fight "for as many days as it takes." Images from his past UN speeches, like the infamous bomb diagram, underscore his stance.

Iran's response could involve proxy attacks on U.S. bases or cyber warfare. The Kurdistan Regional Government has denied allowing its territory for strikes, but threats from Iraqi militias persist.
Conclusion: A Precarious Path Forward
As the world watches, the Israel-Iran war of 2026 unfolds with uncertain consequences. The preemptive strikes on February 28 mark a critical juncture, potentially reshaping the Middle East. Calls for diplomacy remain, but with explosions in Tehran and sirens in Israel, peace seems distant.
Stay tuned for updates as this story develops. For more on the Israel-Iran conflict 2026, follow our blog.